
与单纯经动脉化疗栓塞(TACE)疗法相比,仑伐替尼联合TACE治疗能够延长不可切除肝癌(uHCC)患者的生存率,这为中晚期肝癌的治疗提供了更好的思路。

研究背景
肝癌大国,中晚期多
原发性肝癌是全球第六大常见肿瘤,肿瘤相关的致死率排名第四。约80%的肝癌来自亚洲,近50%来自我国,因此我国是肝癌疾病负担最重的地区。
我国和西方国家的肝癌患者在病因学、流行病学和诊疗实践上各有不同:针对首诊占比约70%的中晚期不可切除肝癌患者,西方国家对中期肝癌推荐以TACE为主的介入治疗,晚期患者推荐系统治疗;我国的CSCO指南和卫健委诊疗规范则对上述不可切除患者均推荐可行TACE治疗,系统治疗的地位相对薄弱。
因此,本研究在现有临床研究及指南推荐的基础上,针对不可切除的肝细胞癌(uHCC)患者群体,对仑伐替尼联合TACE与单纯TACE治疗相比的疗效和安全性进行评估。希望可以进一步补充临床数据空白,为临床治疗提供更多选择。
重要结果
仑伐替尼,保肝护航
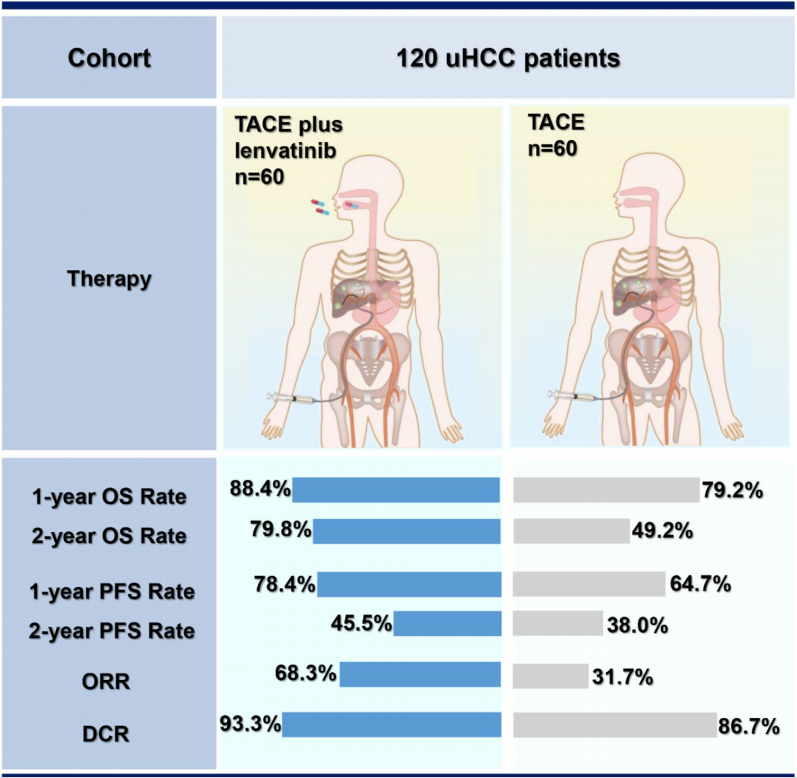
在本研究纳入的120例uHCC患者中,60例接受单TACE治疗,60例接受TACE+仑伐替尼治疗。
从结果看来,TACE+仑伐替尼组对比单TACE组,在以下几个方面均显现优势:
01
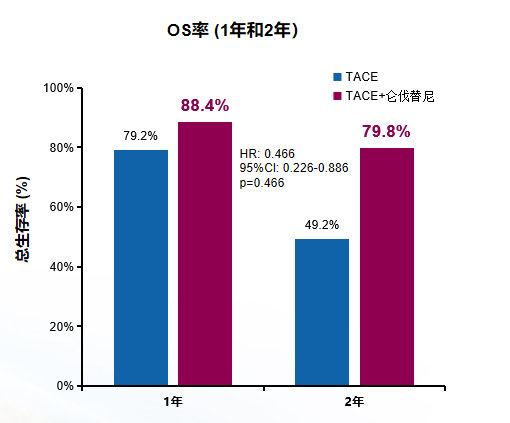
总生存率(OS)
1年和2年OS显著更高(1年OS率:88.4%和79.2%;2年OS率:79.8%和49.2%,p = 0.047)。
02
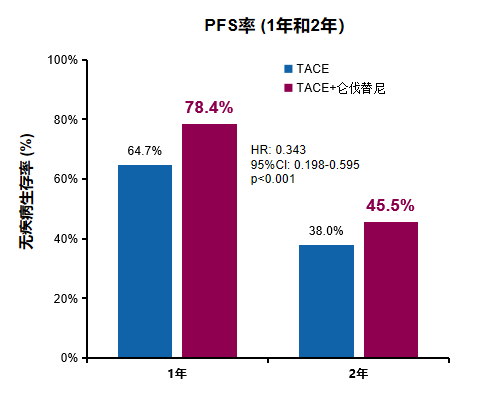
无进展生存期率(PFS)
1年和2年PFS显著更高(1年PFS率:78.4%对比64.7%;2年PFS率:45.5%对比38.0%,p < 0.001)。
03
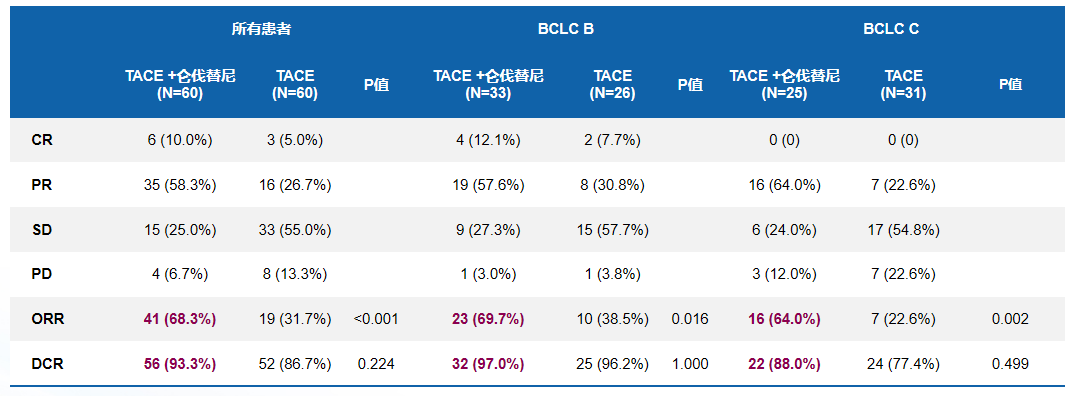
最佳总体客观缓解率(ORR)
TACE+仑伐替尼组的ORR为68.3%,显著高于TACE组(ORR:68.3%与31.7%,p < 0.001),且疾病控制率(DCR)的数值也更高(93.3%与86.7%,p = 0.224)。
04
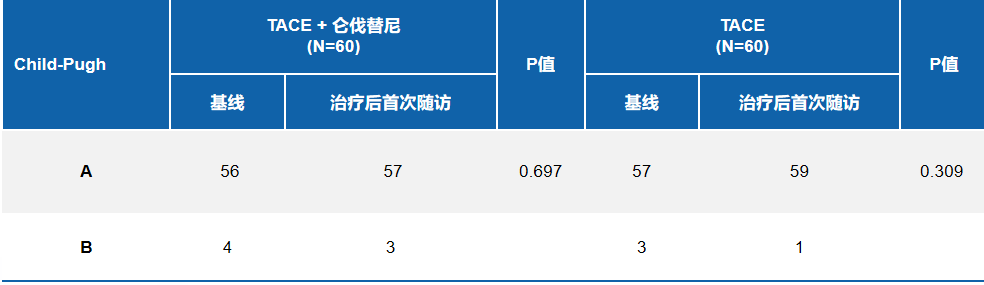
肝功能保护
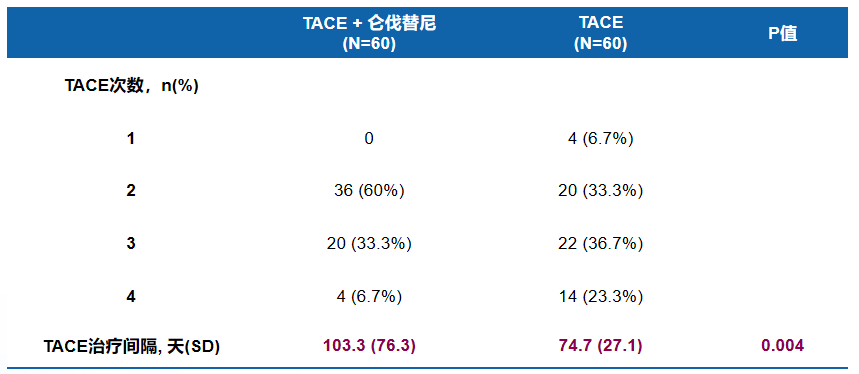
05
后续治疗
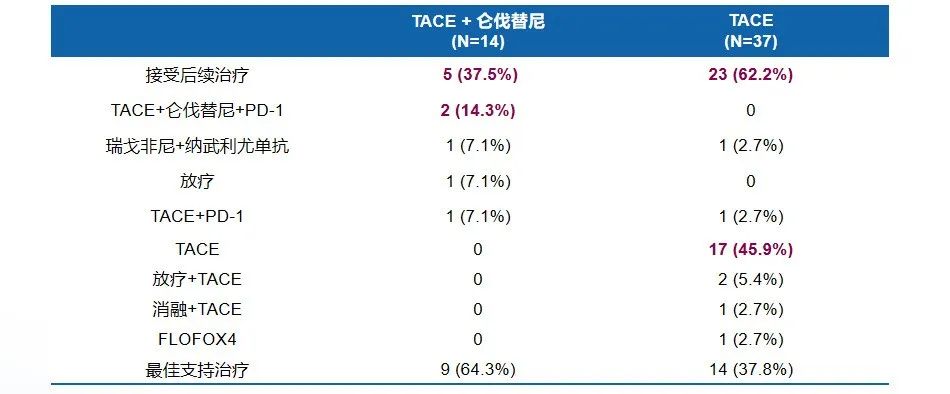
根据以上数据综合评估,仑伐替尼联合TACE在疗效方面可以显著延长生存率、提高总体客观缓解率;在安全性方面不良事件的发生率低,尤其在对于肝功能的维持上具有极大优势;在预后方面能为后续治疗提供更多的选择。
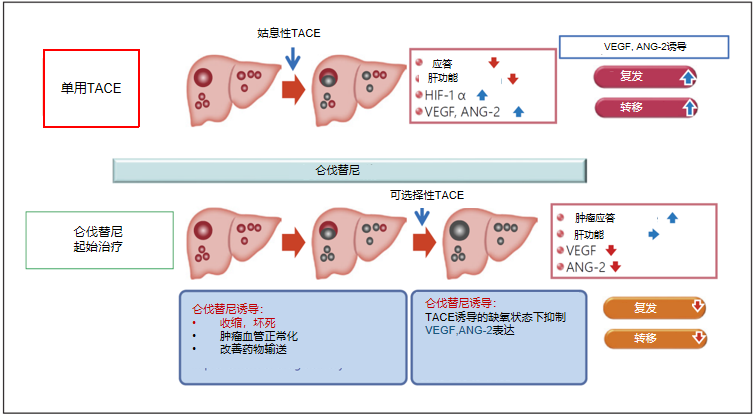
潜在机制
因子受体,多管齐下
临床意义
更多支持,弥补空白
本研究通过回顾性分析,比较了TACE联合仑伐替尼与单TACE的疗效和安全性,弥补了该数据空白,有助于提高介入科专家对系统治疗尤其是仑伐替尼的认识和接受度,为不可切除肝癌的诊疗途径添砖加瓦。
[2]European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address eee, European Association for the Study of the L. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2018;69:182–236.
[3]Xie DY, Ren ZG, Zhou J, Fan J, Gao Q. 2019 Chinese clinical guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: updates and insights. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2020;9(4):452–463.
[4]Matsuki M, Hoshi T, Yamamoto Y, Ikemori-Kawada M, Minoshima Y, Funahashi Y, et al. Lenvatinib inhibits angiogenesis and tumor fbroblast growth factor signaling pathways in human hepatocellular carcinoma models. Cancer Med. 2018;7:2641–2653.
[5]Kudo M, Finn RS, Qin S, Han KH, Ikeda K, Piscaglia F, et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in frst-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised phase 3 noninferiority trial. Lancet. 2018;391:1163–1173.
[6]Ikeda M, Okusaka T, Mitsunaga S, Ueno H, Tamai T, Suzuki T, et al. Safety and pharmacokinetics of lenvatinib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22:1385–1394.
[7]Suyama K, Iwase H. Lenvatinib: a promising molecular targeted agent for multiple cancers. Cancer Control. 2018;25:1073274818789361.
[8]Al-Salama ZT, Syed YY, Scott LJ. Lenvatinib: a review in hepatocellular carcinoma. Drugs. 2019;79:665–674.
[9]Kudo M, Ueshima K, Chan S, Minami T, Chishina H, Aoki T, et al. Lenvatinib as an initial treatment in patients with intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma beyond up-to-seven criteria and Child-Pugh a liver function: a proof-of-concept study. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11(8):1084.
[10]Kudo M. Lenvatinib may drastically change the treatment landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer. 2018;7(1):1–19.













