好医术编辑Alan
深度好文:1433字 | 5分钟阅读
引言
阵发性室上性心动过速简称室上速,是临床上常见的室上性快速性心律失常。阵发性室性心动过速的心电图特征主要包括发作时频率在160-250次/分,节律快而规则,QRS波群形态正常。
读懂室上速体表心电图是作为心血管医生的基础素养,在12月3日我们有请到邹建刚老师进行授课,我们一起来回顾一下吧。
本期主题:
《室上速体表心电图阅读技巧》

以下内容为邹建刚医生12月3日的50%直播课程内容:
室上速体表心电图阅读技巧
一、心电图阅读的几个要点
1. 熟悉正常心电图的特征
2. 观察异常心电图的表现
3. 善于寻找线索
4. 记录长导联心电图
5. 对比不同时间记录的心电图
二、异常心电图的表现:千变万化
1. 心律:窦性?异位?规整?不规整?
2. 心率:快?慢?心动过速?心动过缓?
3. QRS波:窄还是宽?
4. 心房与心室率的比例:1:1?还是n:1?
5. PR间期、QT间期?
6. ST段抬高还是降低?Q波是否异常?
7. T波:高、低、倒、特殊形态?
三、如何阅读心电图:邹建刚老师的选择
Step1:节律?快慢?
Step2:宽、窄?室上性、室性?
Step3:心电图特征?P-QRS-T波是否顺序出现?相互关系?
Step4:与原来心电图对比;
Step5:准备一个好的分规;
Step6:记录长导联心电图;
Step7:病史和体征?胸痛、头寻、晕厥、出汗、血压?有无基础心脏病?心功能?
四、病例分析
病例1
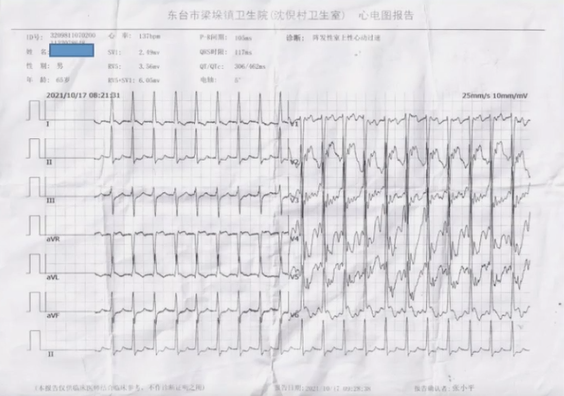
心电图特点:
·窄QRS波心动过速
·RR间期绝对规则
·无P波
初步判断SVT类型是AVNRT、AVRT或者是AT?
窦性节律和室上速发作的心电图对比:arrow_down:
(点击放大查看)
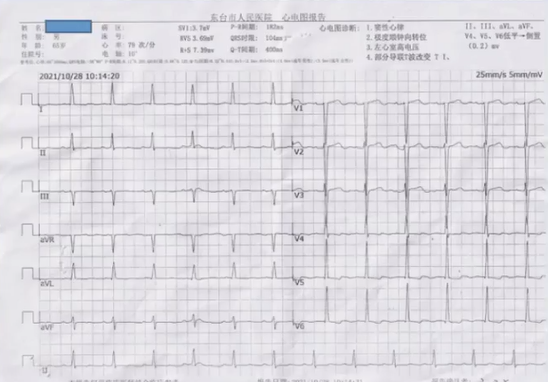
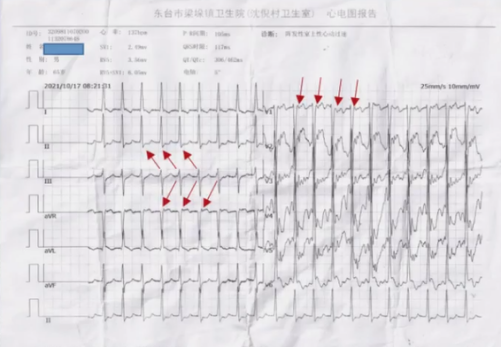
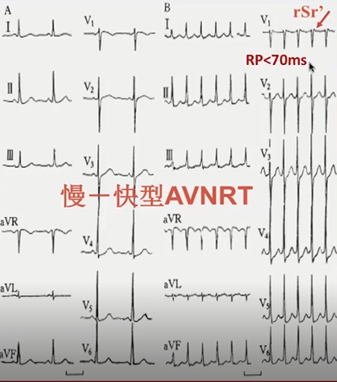
由对比图可分析出这是典型AVNRT体表心电图特征:II、III、AVF:假性S波;V1:rSr’【假性r波】
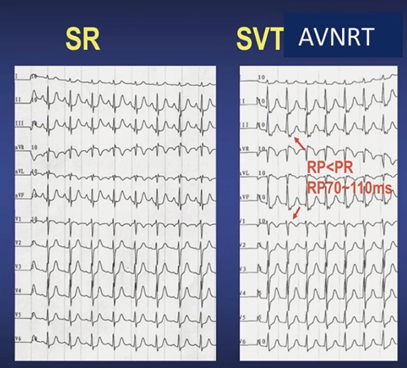
病例2
心电图特点:
·窄QRS波心动过速
·RR间期绝对规则
·无窦性P波
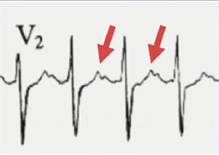
由此可以初步确认是AVRT,仍然需要进一步排除AT。
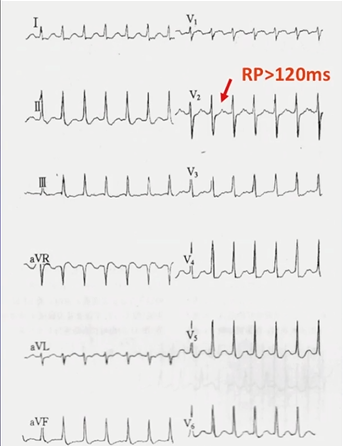
病例3
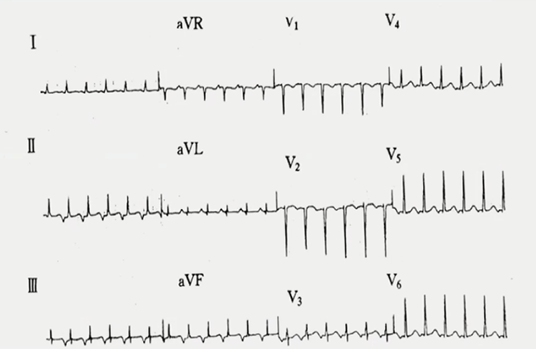
心电图特点:
·窄QRS波心动过速
·RR间期绝对规则
·P’波
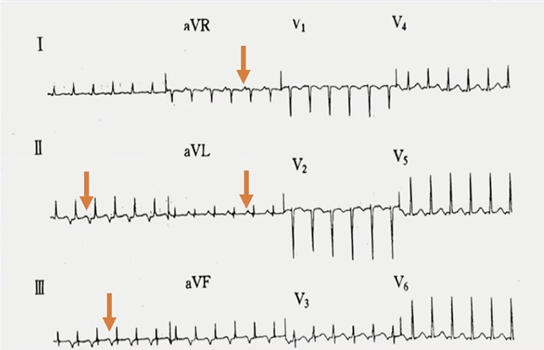
RP>PR,由于起源于低位右心房,可以初步判断为AT,但是需排除F-S型AVNRT和PJRT。
病例4
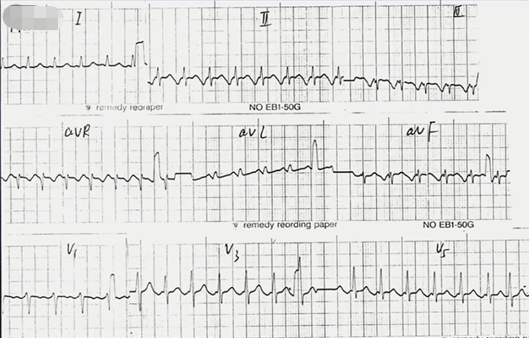
心电图特点:
·窄QRS波心动过速
·RR间期绝对规则
·P’波,RP>PR
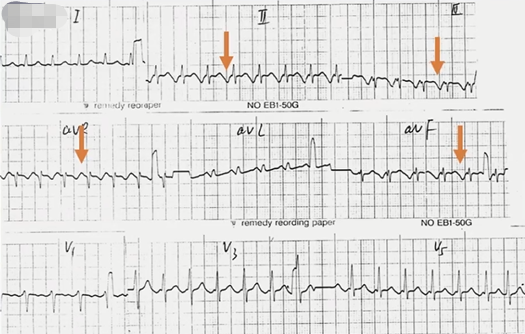
由上图箭头处得出是持续性交界性反复性心动过速(PJRT)。
五、几个关键注意点!
1. 对比基线、以前的心电图,寻找线索
2. 右束支比左束支容易发生频率相关的阻滞
3. 旁路同侧束支发生阻滞:心动过速频率减慢
4. 迷走神经刺激或ATP注射终止心动过速进行对比分析