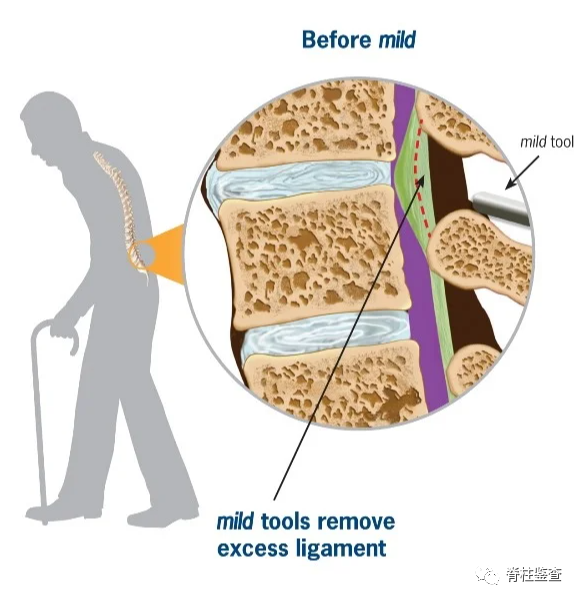
参考文献
[1]Rousing R, Jensen RK, et al. Danish national clinical guidelines for surgical and nonsurgical treatment of patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J. 2019 Jun;28(6):1386-1396.
[2]Rousing R, Jensen RK, et al. Danish national clinical guidelines for surgical and nonsurgical treatment of patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J. 2019 Jun;28(6):1386-1396.
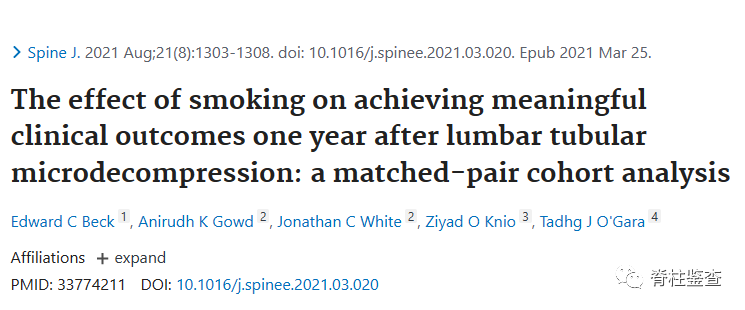
[3]Beck EC, Gowd AK, et al. The effect of smoking on achieving meaningful clinical outcomes one year after lumbar tubular microdecompression: a matched-pair cohort analysis. Spine J. 2021 Aug;21(8):1303-1308.
[4]Melcher C, Paulus AC, et al. Lumbar spinal stenosis - surgical outcome and the odds of revision-surgery: Is it all due to the surgeon? Technol Health Care. 2022;30(6):1423-1434.
[5]Goel SA, Modi HN. Reoperations Following Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis. Indian J Orthop. 2018 Nov-Dec;52(6):578-583.
[6]Gulati S, Nordseth T, et al. Does daily tobacco smoking affect outcomes after microdecompression for degenerative central lumbar spinal stenosis? - A multicenter observational registry-based study. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2015 Jul;157(7):1157-64.
[7]Sandén B, Försth P, et al. Smokers show less improvement than nonsmokers two years after surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis: a study of 4555 patients from the Swedish spine register. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011 Jun;36(13):1059-64.
[8]Nerland US, Jakola AS, et al. The Risk of Getting Worse: Predictors of Deterioration After Decompressive Surgery for Lumbar Spinal Stenosis: A Multicenter Observational Study. World Neurosurg. 2015 Oct;84(4):1095-102.
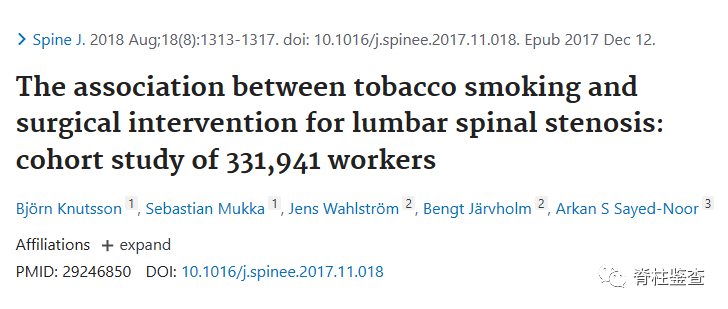
[9]Knutsson B, Mukka S, et al. The association between tobacco smoking and surgical intervention for lumbar spinal stenosis: cohort study of 331,941 workers. Spine J. 2018 Aug;18(8):1313-1317.