以下文章来源于江苏牙体牙髓 ,作者闫明 译
原文网址:http://endodontics.styleitaliano.org/radiculous-small-molars-molarized-premolars-three-canalled-maxillary-premolars-how-to-identify-and-manage-them/
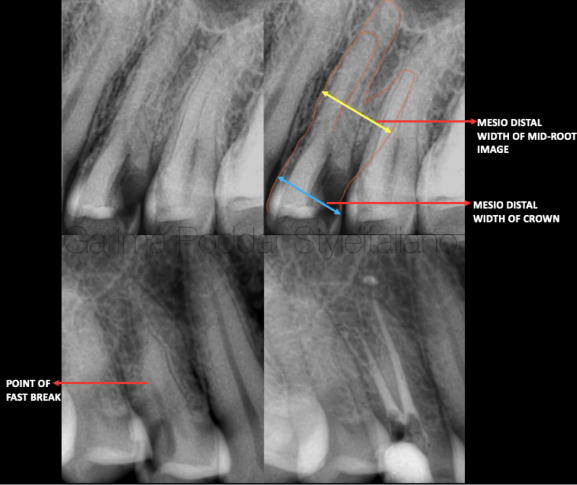
图1. 当分析根尖片时,设备和技术可以帮助我们发现三根管前磨牙:
)Sieraski等学者提示当上颌前磨牙根中段影像的近远中径等于或大于牙冠的近远中径时,则此牙可能存在三根管。
b)两到三张不同角度的术前片可以了解更多的牙根和根管结构细节。
c)如果颊侧根管存在分叉:发现根管影像的突然消失点则提示额外根管的存在。
Tools and techniques helpful in detection of a three canalled premolar are as follows-
Tip while reading the radiograph-
a). Sieraski et al suggested, that a maxillary premolar is likely to have three roots when the mesio-distal width of the mid root image is equal to or greater than the mesio-distal width of the crown.
b). 2-3 intraoral pre-operative x-ray images at different angulations could give more details of the roots and canal configuration.
c). In case of a split of the buccal canals – identifying a point of “fast-break” could hint the presence of extra canal.
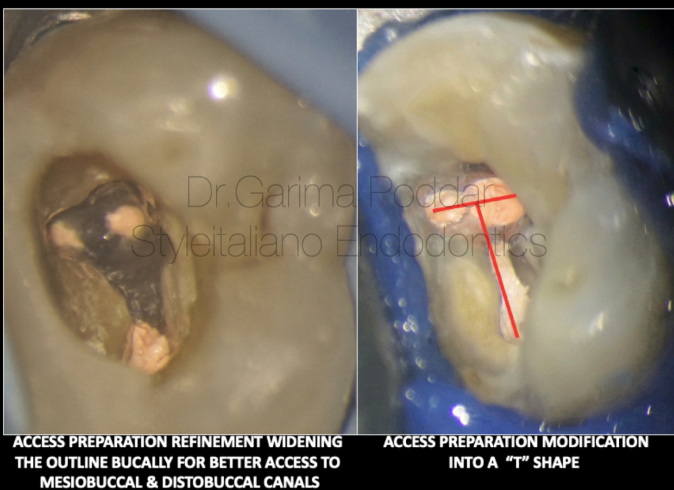
图2. 髓腔入路的调整:三根管的上颌前磨牙的髓腔入路洞形需要扩展颊侧的近远中向外形以允许颊侧两个根管的便利进出。将洞型扩展成“T”形以便于定位近颊和远颊根管,以及器械的顺利进入。
Tips for acces cavity modifications-
Maxillary premolars with three canals need access cavity refinement by broadening the outline on the buccal aspect mesio-distally to permit good access to each of the two buccal canals.
Extending the cavity design into a “T” shape helps locate and instrument the mesio buccal and disto buccal canals with ease.
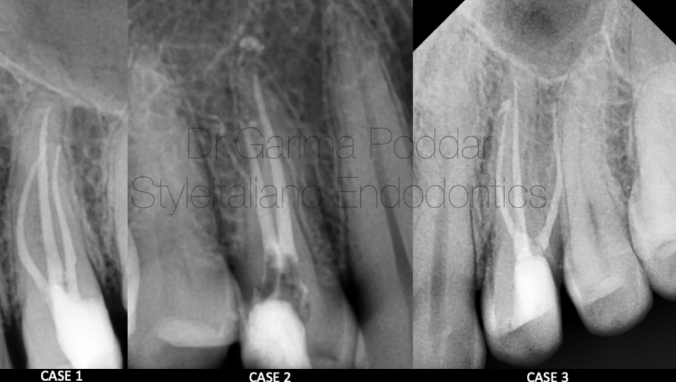
图3. 根管的成形:认清颊侧细小根管成功治疗的要点,不要对根管进行过度的扩展预备,否则会导致“带状侧穿”的发生。此类牙根通常非常细长。
Tip while shaping the canals-
While shaping, its important to understand that for successful management of the narrow buccal canals, over enlargement should not be attempted as excessive canal preparation could result in a lateral “strip” perforation. The roots are usually very slender and narrow in such teeth.
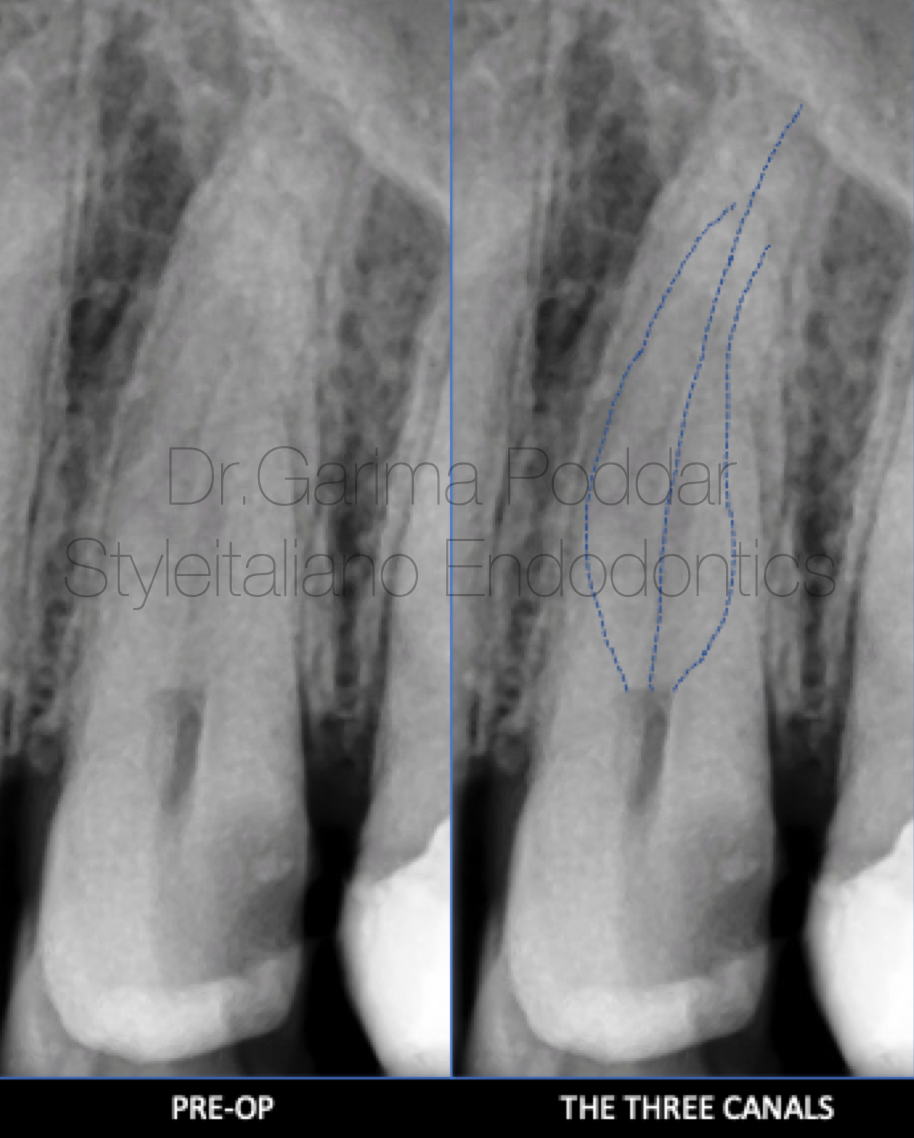
图4. 病例一:患者男,35岁。因左上后牙区疼痛伴触痛前来就诊。临床检查发现24、25存在症状。借助牙髓检测、临床及影像学评估诊断为24慢性不可复性牙髓炎。术前片中,追踪微弱的投射线提示上颌第一前磨牙存在三根管。
A 35 year old male patient reported to our hospital with pain and tenderness in maxillary left posterior region.
On clinical examination it was observed that tooth number 24 and 25 were symptomatic.
Diagnosis of chronic irreversible pulpitis was made with the help of pulp tests, clinical and radiographic evaluation.
On the pre-operative x-ray, faint radiolucent lines could be traced guiding towards the presence of three canals in maxillary first premolar.
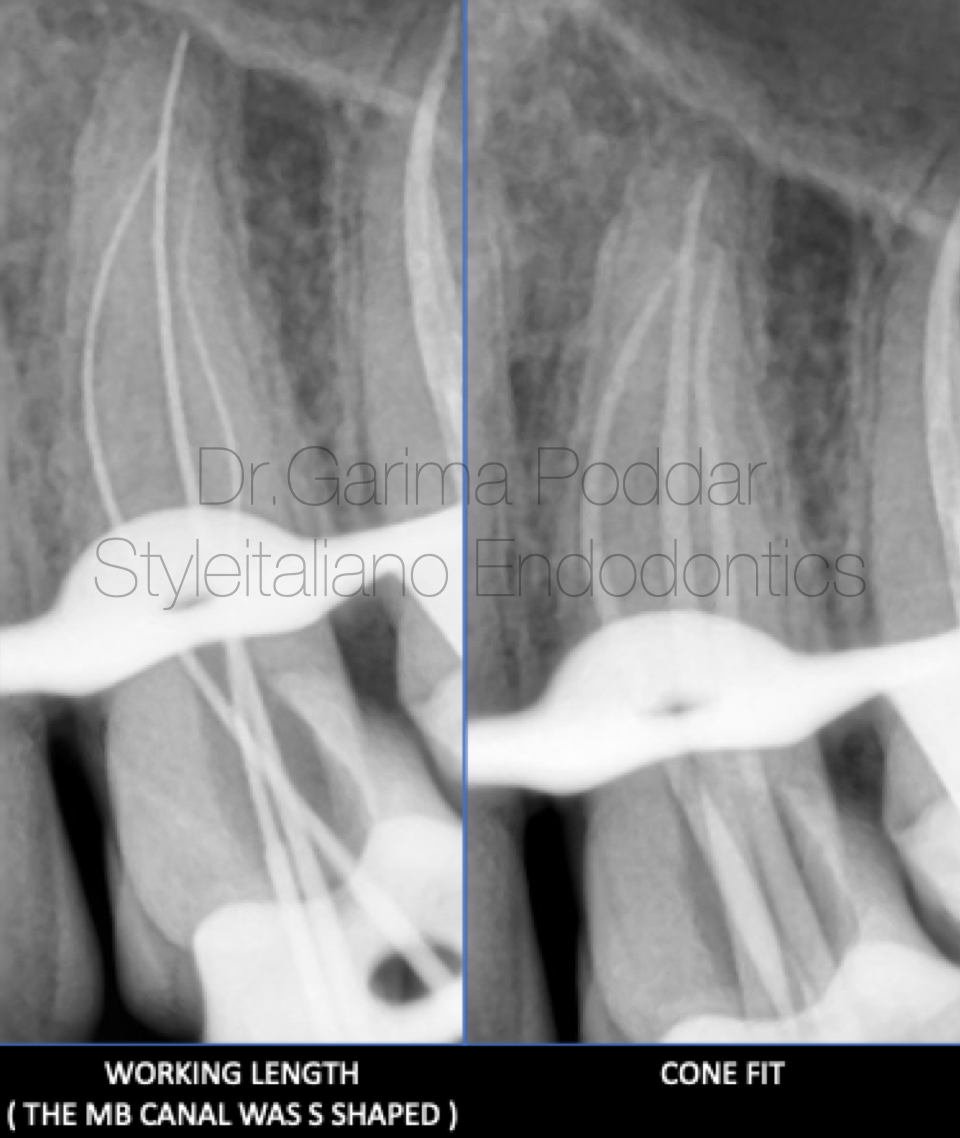
图5. 局部麻醉,橡皮障隔离。入路预备,远中制作假壁。
根管成形:所有根管使用开口锉冠方预敞。8#、10#手用K锉疏通根管,根尖定位仪确定工作长度并拍摄插针片确认。疏通锉顺滑根管,根管成形至25#04锥度。
根管冲洗:5.25%次氯酸钠,蒸馏水和17%EDTA彻底冲洗根管,超声活化冲洗液。
根管充填:选择合适主尖。生物陶瓷糊剂结合单尖法充填。
Local anesthesia was administered and rubber dam isolation was done. Access preparation was done and a pre-endo build up was done.
Shaping protocol-
Coronal flaring with one flare file(Micromega, France) was done for all three canals.
Hand instrumentation with 8K, 10K, files was performed till working length which was determined using electronic apex locator and confirmed on a radiograph.
OneG files were used for glidepath preparation and shaping was done up till 25-04% files using 2 shape files ( Micromega, France).
Irrigation protocol-
5.25% sodium hypochlorite, distilled water and 17% EDTA were used for thorough irrigation and the solutions were ultrasonically activated.
Obturation protocol-
Cone fits for all three canals were confirmed. Bio ceramic sealer( Ceraseal, Meta biomed) with single cone was the technique of obturation for this case.
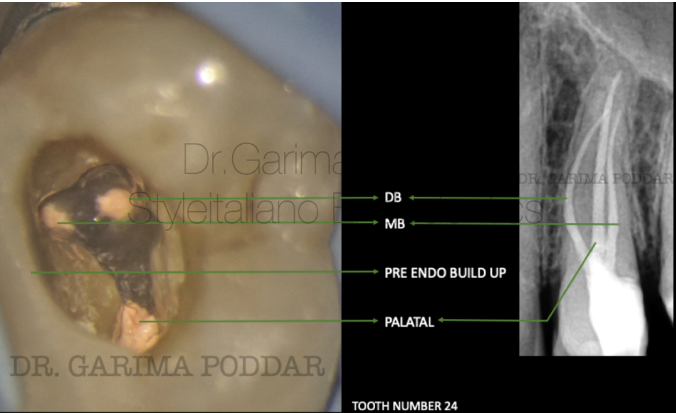
图6. 根管治疗后自酸蚀技术堆塑树脂核。转诊进一步行间接修复。
Core build up post endodontic treatment was done using paracore (coltene).
The case was referred for further prosthetic rehabilitation to referring dentist.
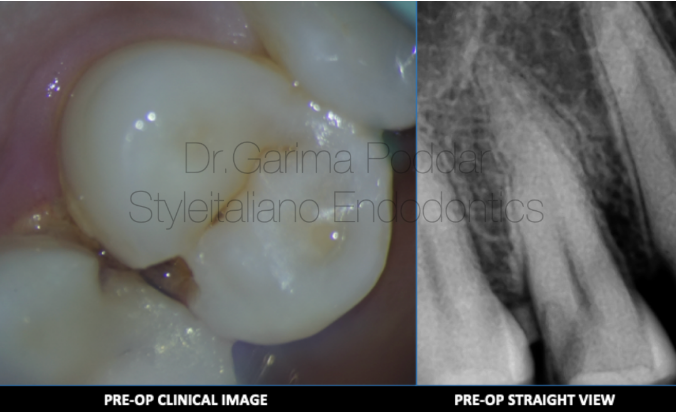
图7. 病例二:患者女,37岁,右上颌第一前磨牙剧烈疼痛伴触痛20天。临床检查14深龋洞,叩痛(+)。影像学检查确诊14不可复性牙髓炎。
影像学检查显示:1. 远中邻面透射影波及牙髓;2. 颊侧根管根尖三分之一区域不寻常的解剖结构。
A 37-year-old female patient reported to our hospital, with severe pain and tenderness in maxillary first premolar of right side for 20 days. On clinical examination, a deep carious lesion was observed in tooth number 14.
The tooth was tender on percussion. Radiographic examination confirmed the diagnosis of irreversible pulpitis in 14.
Radiographic evaluation revealed the following-
1. Deep disto proximal decay in 14 involving pulp.
2. An unusual anatomy in the buccal canal in apical third region.
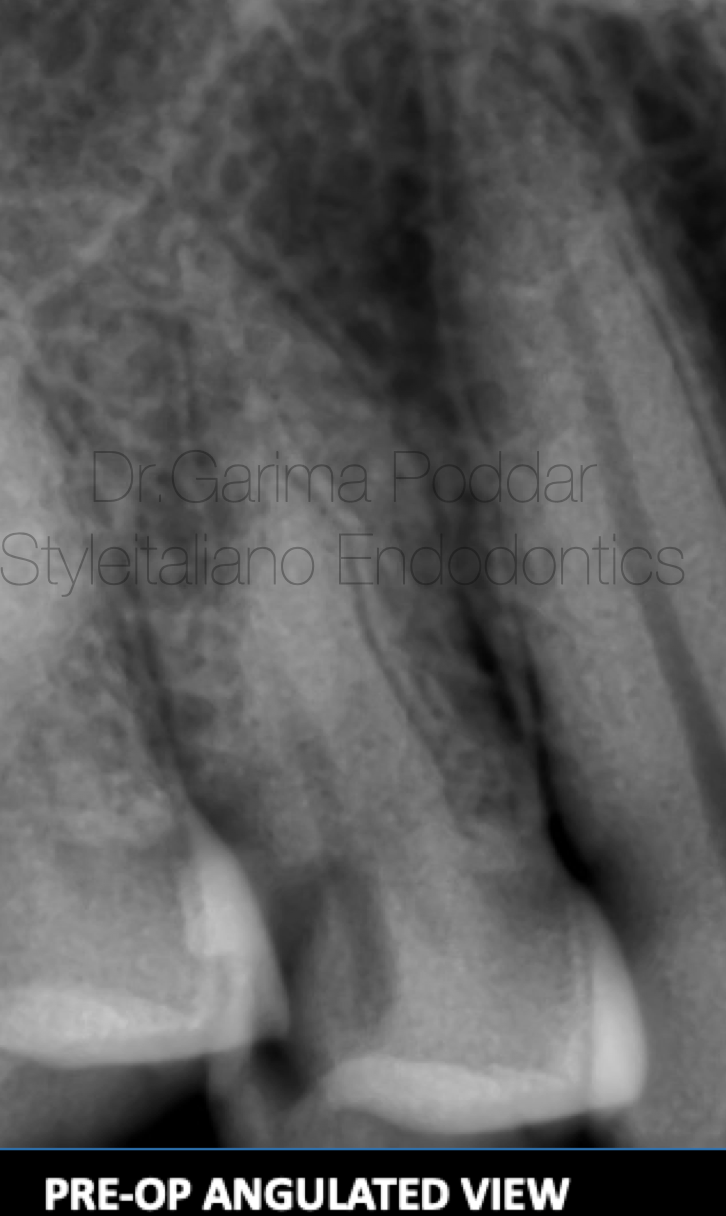
图8. 橡皮障隔离患牙,彻底去龋,髓腔入路预备。最初只有颊侧和腭侧两个主根管。后来采用偏移投照技术发现根管透射影存在一个“突然消失”点,根管中下段很难追踪透射轮廓。暗示根管存在分叉等非典型的解剖结构。使用8#和10#K锉探查颊根疑似分叉,借助牙科显微镜的放大和照明非常的有帮助。此外,对术前片的详细分析为不寻常解剖结构的存在提供了线索。
根管成形:冠方预敞,10#K锉扩大通畅分叉根管,通道锉顺滑根管。腭根和近颊根成形至25#06锥度。远颊分叉K锉手动预备至20#。
The tooth was isolated using rubber dam isolation and caries was excavated completely.
Access preparation was done. Initially only two main canals, that is buccal and palatal canals could be negotiated. Later on, angulated view radiograph was made using tube shift technique, and a point of “fast break” was seen after which the radiolucent canal outlines were not easily traceable on the x-ray.
This hinted towards presence of a split and an atypical canal anatomy. A buccal split was suspected and then it was scouted using an 8K and 10K files. The treatment was performed under magnification, using a dental operative microscope, which proved to be really helpful because of better magnified view and good illumination. Also, a detailed study of the pre-operative radiograph provided a clue for the presence of an unusual anatomy.
Shaping Protocol -
Coronal flaring was done using One Flare File (Micromega, France).
10K file was used to instrument the canal till in became loose in both the splits
Glide path preparation was done with the help of One G File (Micromega, France).
The palatal canal and mesio buccal canals were shaped using One-Reci Files (25-06%) (Micromega, France). The distobuccal split was negotiated first using manual K files number 8 and 10 and then with the help of a gyromatic hand-piece – K400, further shaping was done till 20K file for this split.
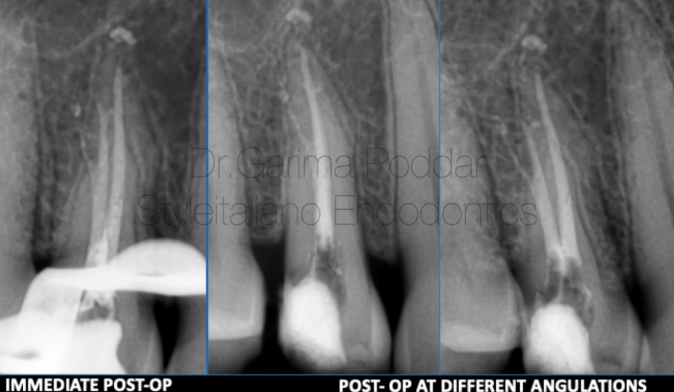
图9. 根管冲洗:预备成形过程中,每次更换锉使用5.25%次氯酸钠冲洗。使用30G侧方开口针头注射器。根管成形后,对所有根管行终末冲洗及超声活化:1. 17%EDTA每根管1ml,超声激活;2. 蒸馏水冲洗;3. 5.25%次氯酸钠,超声激活;(每根管循环重复4次)4. 蒸馏水。
根管充填:纸捻干燥根管,拍摄试尖片。分叉颊根充填时使用纸捻封闭其中一个分支,牙胶充填另一个分支,然后牙胶替换纸捻充填封闭。采用热牙胶垂直加压技术结合AH Plus糊剂充填根管。
Irrigation Protocol
Throughout shaping, 5.25% sodium hypochlorite was used after each file. Side vented 30 gauge needles were used for irrigation.
After shaping, the following protocol in each canal, was used for irrigation and activation of irrigants-
1. 17% EDTA – 1ml per canal – ultrasonic activation.
2. Distilled water used to flush the canals.
3. 5.25 % sodium hypochlorite - ultrasonic activation. (4 such cycles repeated per canal)
4. Distilled water.
Obturation Protocol
Canals were dried with paper points. Cone fit intra oral radiograph was made.
One split was blocked by inserting a paper point and gutta percha cone was inserted in the other split and then the paper point in the other split was also replaced with cone. Canals were obturated with warm vertical compaction technique using EQ-V (Meta Biomed). Sealer used was Ah Plus (Dentsply Maillefer).
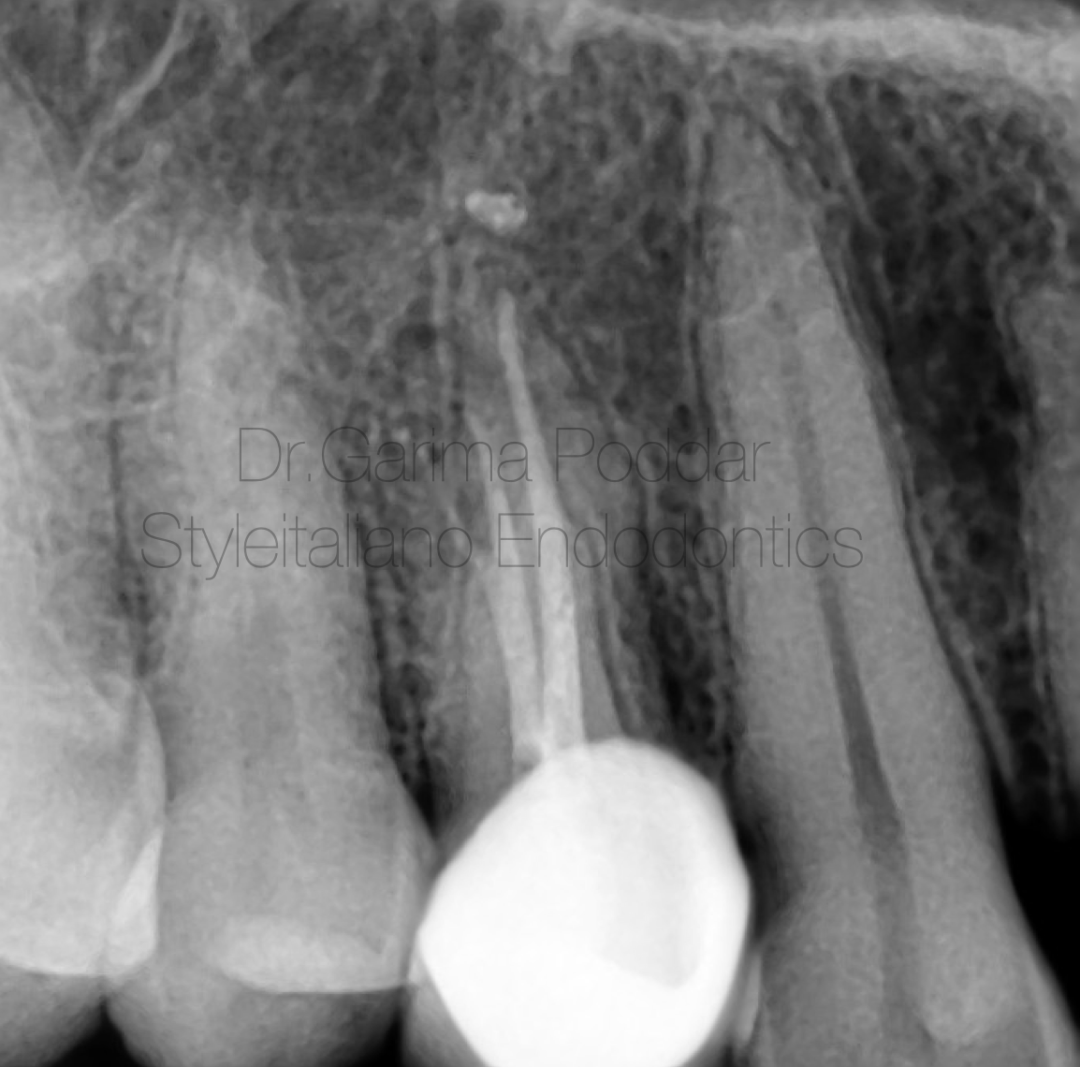
图10. 根管治疗和修复后根尖片。复合树脂塑核,全冠修复。
Post Endodontic Restoration
Core build up was done for 14, using composites. A full coverage crown was given on 14.
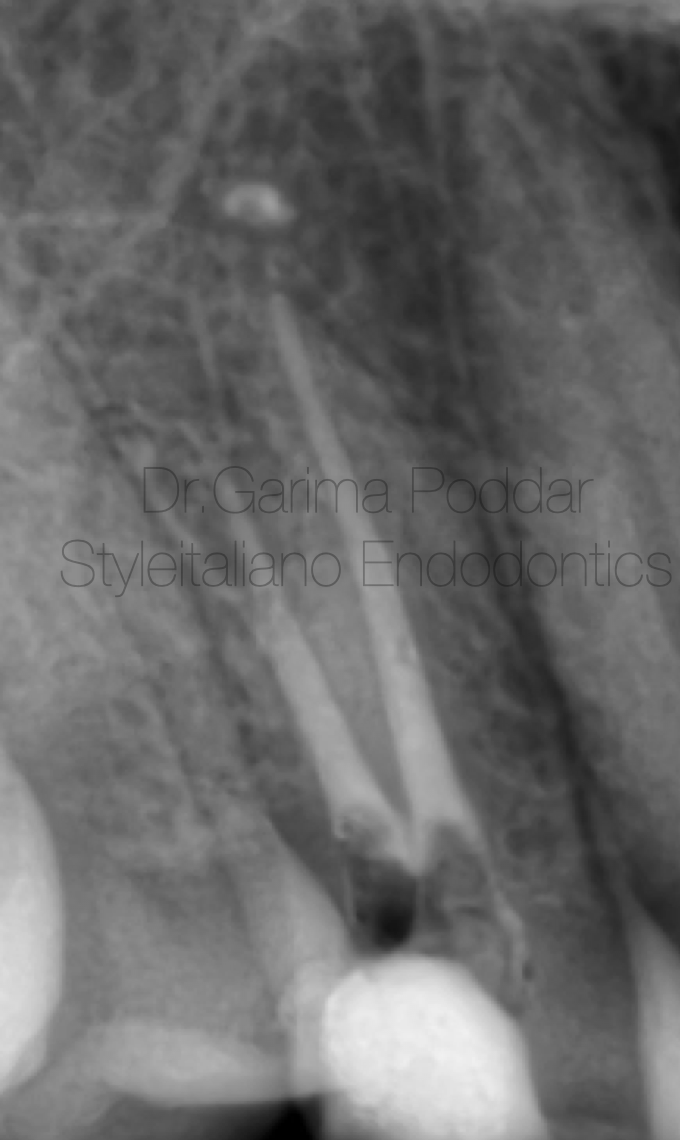
图11. 有时,两个颊侧根管从一根普通的狭窄根管中出现,根管口的预敞有助于更简单的探查和预备各个分支。
Sometimes, the two buccal canals emerge from a common narrow canal which originates from the pulp chamber.
In this case also, same configuration was encountered.
Pre-flaring the canal orifice, makes the negotiation and instrumentation of such deep splits easier.
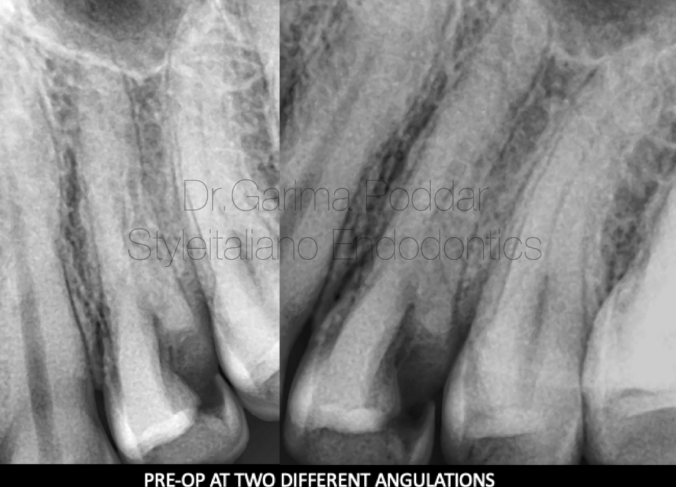
图12.
病例三:患者男,44岁,因左上后牙疼痛伴触痛10天就诊。检查显示患者存在持续痛,24 叩痛,远中邻合面深龋洞,伴食物嵌塞。诊断为急性不可复性牙髓炎。在术前片中观察到以下细节:1. 远中邻面深龋伴牙髓暴露;2. 髓腔透射影不清。
A 44 year old male patient reported with pain and tenderness since 10 days in maxillary left posterior tooth to our hospital.
On examination it was observed that the patient has continuous pain and tooth number 24 was tender on percussion. There was a deep proximal decay present, and patient also complaint of food lodgement.
A diagnosis of acute irreversible pulpitis was made.
On pre-operative radiographs the following details were observed-
Deep disto proximal decay with pulp exposure.
Sudden loss of radiolucency in the pulp chamber.
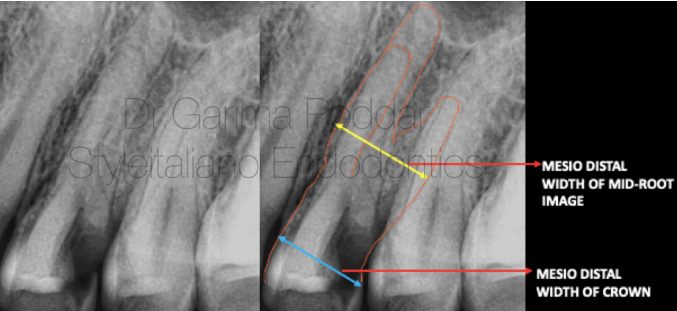
图13. 根中段近远中径明显大于牙冠近远中径。
Mesio-distal width of mid root greater than the mesio distal width of the crown.
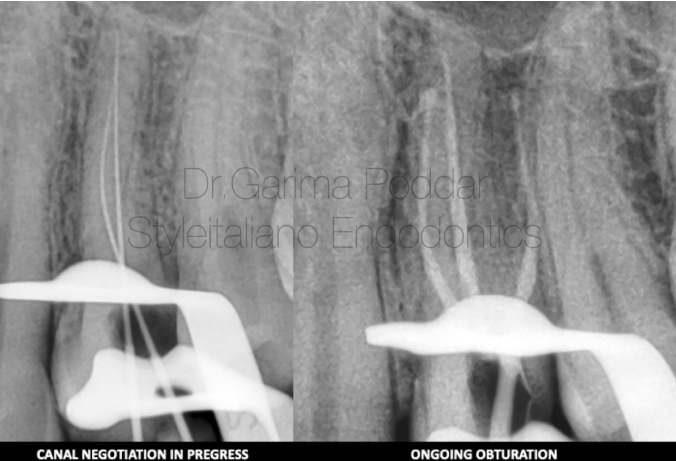
图14. 局部麻醉,橡皮障隔离,去腐,预备髓腔入路。修整拓宽颊侧洞形至“T”形,发现近颊、远颊及腭根三根管。
根管成形:冠方预敞,8#、10#手用K锉疏通根管以便于通道锉的进入,成形根管。
Local anesthesia was administered.
Rubber dam isolation was done.
Caries was excavated and access preparation was done. The access cavity was modified into a ”T ” shaped design with more widening than usual of the buccal aspect.
Three canals, namely- mesio buccal, disto buccal and palatal were found.
Shaping Protocol
Coronal flaring was done using One Flare File (Micromega, France).
Hand instrumentation was done with 8 and 10 K files followed by which glidepath was prepared with the help of one G file( Micromega).
Shaping was done using 2 shape files ( Micromega, France).
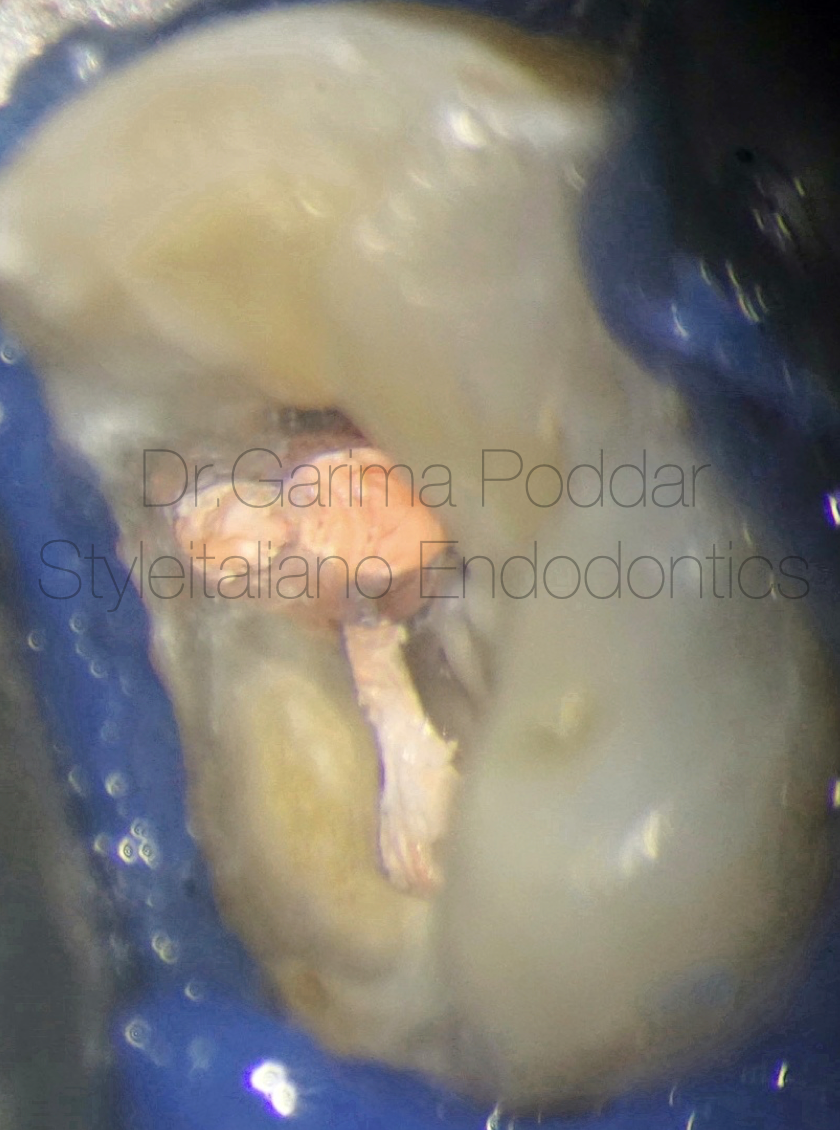
图15. 根管充填:确定主尖根尖可卡紧,生物陶瓷糊剂结合单尖法充填根管。
Obturation protocol-
Master cones were finalised after confirming their tug backs.
Bioceramic sealer (Ceraseal, Meta biomed) with single cone was used for obturation.
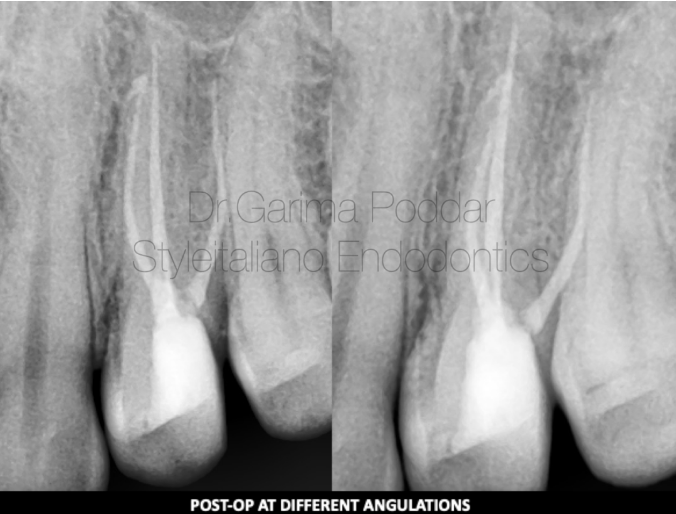
图16. 复合树脂塑核。
Post endodontic core build up was done using warm composites.
总结
In depth knowledge of variations in the root canal anatomy is important in order to not miss an anatomy during endodontic treatment of a tooth.
In today’s practice, due to use of advanced tools like magnification, good illumination and radiography tools like CBCT, chances of diagnosing and treating atypical anatomy has increased by many folds.
免责声明:本文来源于网络,仅供医生学习交流,如有侵权,请联系删除!